
Suppose that you want to visit some unknown place then how to reach that place? The answer is very simple, by using a map. Let’s make it more interesting, if you don’t have that map then? Hmm… Okay, then what if part of your brain could rush ahead of you, quickly sketch a map, and feed it to the rest of your brain to help you find your way? It seems foolish but you may be surprised to know that self-driving cars are working in the same way. It uses neat 3D map-making technology which is known as LIDAR. Oh… It sounds similar to RADAR but is different from that. How? Let’s find out.
Why And What is LIDAR?
Just look around yourself. What do you see? It is a 3D color map of your immediate environment that your brain has built by using the light rays soaked up by your eyes. In the same way, a robot has to draw a 3D map by using a couple of digital eye cameras. If we see as a human being, we know these things because your brain processes visual information using experience. But in the case of machines or robots, they don’t have the same deep life experience to draw on, which means they are having a natural disadvantage when it comes to “seeing” the nearby environment.

LIDAR on drone
That is a big reason why self-driving cars often prefer to look at the world a different way, using the LIDAR (Light Detection and Ranging) system instead of any digital camera. As we have seen that where the digital camera took a 2D picture to calculate the nearby environment where LIDAR makes millions of measurements of depth information in all directions (3D map) simultaneously. The main significance of this system is that it is a faster and easier way to turn the capture information into a 3D map for navigation, in real-time.
When saw a self-driving car you may probably found a helmet-like object over it. That is LIDAR. This object transmitted or emitted invisible laser beams in all directions and catching the reflections to calculate the distance from nearby obstacles. So, the basic working principle of LIDAR is similar to RADAR.
Engineering Inside:
A complete LIDAR system is made of several important components. All of the components work together to generate and geo-reference the data and some of them are given below:
- LIDAR source, detector, and scanning mechanism
- Timer circuit
- GPS
- Inertia Measurement Unit (IMU)
- Computer
LIDAR Source, Detector, And Scanning Mechanism:
The LASER (Light Amplification and Stimulated Emission of Radiation) source generates the energy of the pulses. The laser used in the LIDAR system is having low energy and safe for human eyes. The detector unit receives the laser light pulses that are reflected from the target objects. The scanning mechanism is specifically designed to make consistent scanning by using laser pulses.
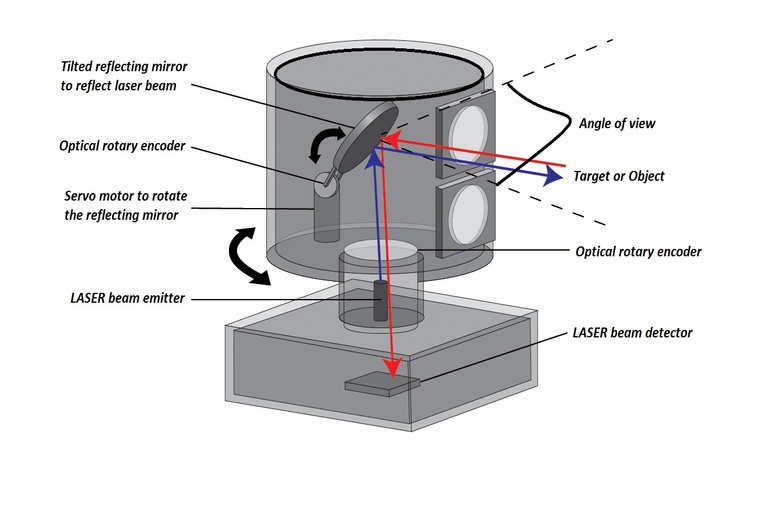
Laser source and receiver diagram of LIDAR system
Timer Circuit:
This circuit records the exact time the laser pulse leaves and returns to the scanner. Every transmitted laser pulse can have up to multiple returns as it is reflected off of objects on the surface. Every returned pulse must be precisely timed to ensure an accurate measurement. And all the timing related parameters are controlled by this electronic board.
GPS:
All of us are aware of the GPS receiver system and most of us have used it while traveling towards new places. The GPS unit in the LIDAR system records the precise x, y, and z positions of the scanner. To improve the accuracy most of the LIDAR uses a fixed ground reference station. This ground station has a known location and is used to correct and improve the collected data of lidar sensors. The GPS with IMU allows for the direct geo-referencing of the points.
Inertial Measurement Unit (IMU):
This unit contains an accelerometer, gyroscope, and magnetron sensors that measure the velocity, Orientation, and gravitational forces.
Computer:
A reliable computer system is required to make sure that all of the individual components of the system are working properly. The computer system integrates the data from the Laser system, GPS, and IMU to produce useful data for further calculations.
Working Process:
In the LIDAR system laser source emits pulses in all directions to get the 3D map. Reflected pulses are detected by the laser receiver. Controlling of pulse duration is done by an electronic timer circuit. The current generation of laser scanners sends up to 106 pulses of light per second to the target and measures how long it takes each pulse to reflect the receiver unit. These times are used to calculate the distance of each pulse traveled towards the target. The GPS and IMU units determine the precise target position and the exact coordinate is calculated for each point. That’s how the LASER pulses can create a 3D map for various observations.
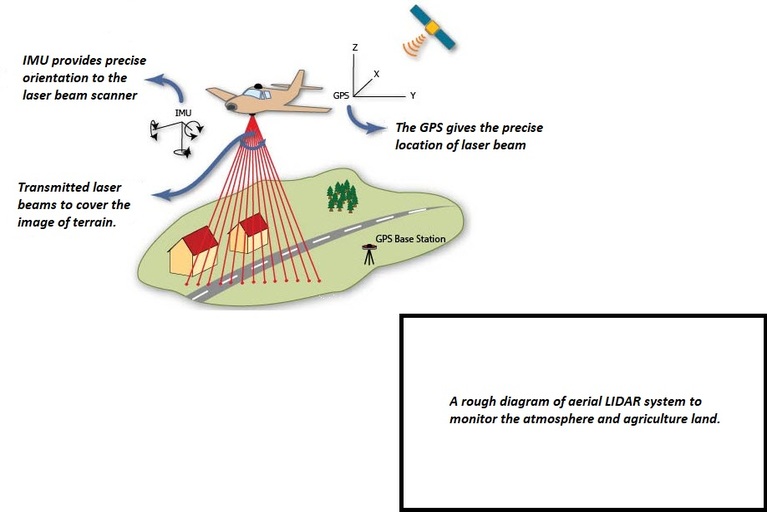
Working process of LIDAR in aerial system
Application:
As of now, we have seen autonomous robots and self-driving cars are using the LIDAR system. We can also use LIDAR to study the gas composition of the atmosphere. The most common applications of the LIDAR system to date are in geographical and atmospheric mapping.
Thanks for reading. See you soon with another exploration!





