
In the modern communication era, cell phone technology marches relentlessly forward. Today everyone is using mobile phones for communication purposes. These mobile phones are working on the cellular network system. As we know cell phone communication has evolved from 1G to 5G and it will go further in upcoming years. The major limitation of cellular communication or mobile phone communication is that it primarily depends on the ground-based cell phone network (or mobile signal towers). In remote areas or cases of natural calamity, these cell phone towers are not able to provide communication. Here a satellite phone proves its mettle. Satellite phones fearlessly go where cell phones can’t. Let’s have a brief intro to the satellite phone.
What is this?
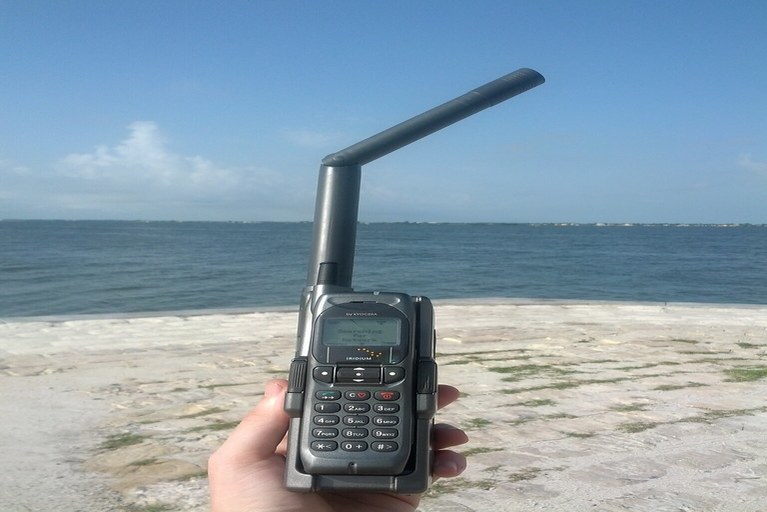
Satellite phones are similar to your mobile phones. They let make you phone calls from almost anywhere on the earth. Its communication does not rely on terrestrial cell phone networks or cellular communication. Instead, satellite phones beam their data directly to and from satellites (those are orbiting the earth).

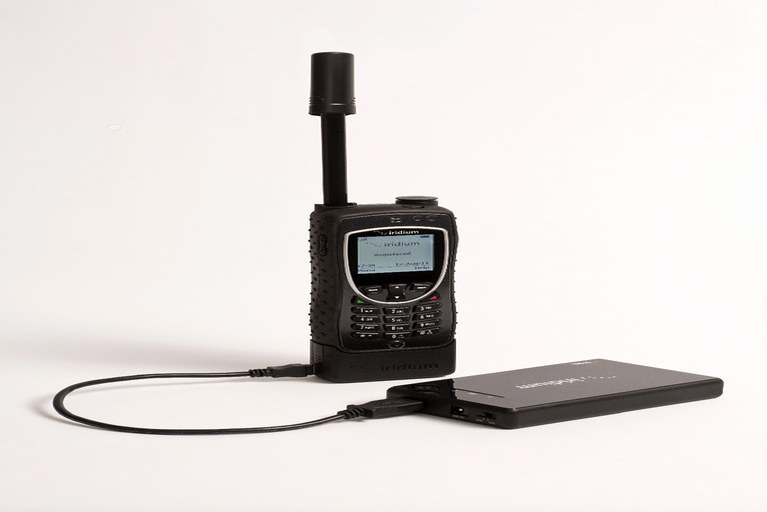
Satellite phone
Based on their functionality we can say a satellite phone is a phone that uses satellites for communication (for sending and receiving data) instead of terrestrial lines. Typically, these gadgets are enabled communication all over the world irrespective of location whereas normal cell phones require proper terrestrial network coverage to enable communication.
Units involved in Satellite phone communication:
Satellite phone communication includes below units:
- Satellite network
- Ground stations
Satellite network:
Satellite phone systems work very differently depending on the technologies each manufacturer deploys in their product. Some companies designed their satellite phones based on GEO synchronous satellites, while others use LEO (Low Earth Orbit) systems. Each satellite system has its own merits and demerits.
Satellite network for communication
GEO stationary systems:
This system uses geostationary satellites (also known as GEO orbit (Geostationary Equatorial Orbit) or High orbit satellites). These satellites follow the Earth as it spins. As of result these satellites much remain in a fixed position in the sky with respect to any point on Earth. They maintain a high altitude orbit, at around 36000 kilometers, and they are always centered above the Earth’s equator.
Merits:
These are vast, very powerful satellites and just one of them can serve a large geographical area on the Earth’s surface. With a constellation of only three satellites, we can cover the whole Earth. Satellites in GEO orbit are specifically designed to handle huge volumes of data; it means they can handle voice as well as video streaming data, television channels data, and much more. Two major companies INMARSAT and THURAYA are using GEO synchronous configurations.
Demerits:
The downside of this configuration is that their high altitude causes significant transmission delays of around 200 to 250 milliseconds one way. So, when one user asking a question to another user then he or she needs to wait for a few moments before them answers him or her questions.
Also, geostationary satellites hover over the equator line; they do not provide much coverage for the northern and southern poles.
The biggest limitation to the geostationary system is related to size. To make the connection with satellites user needs a device that’s roughly the size of a laptop; much of the bulky because of the directional antenna. And also user needs to calibrate the antenna and then point it towards the satellite to receive the data efficiently and effectively.
LEO system:
LEO satellites spin in the lower orbit of earth that is approximately 1500 kilometers. These systems are operated by companies like GLOBALSTAR and IRIDIUM. When we are going to compare the GEO synchronous and LEO system then we can say that the first one gorilla of the industry and the second one is the mosquito.
Because LEOs are so low in their orbits, a network might require as many as 60 to 66 satellites to provide coverage for most of the world. At any one time, a user may be within the range of two or more LEO satellites. These satellites complete the entire orbit in around two hours.
Fast-moving satellites in LEO orbit mean reliable service for much of the planet. So, if you are in an emergency then you can rely on LEO satellites for communications.
Merits:
LEO satellite phones are known for superior call quality, lower transit time, and greater dependability. They also need less power as compare to GEO satellite phones.
Demerits:
Data transmission and reception rate are low as compare to GEO synchronous system.
Whether you are using a GEO synchronous or LEO system, for best service, your satellite phone needs a line of sight view to the satellites. As of result, you need to step outside to make a call.
Ground stations:
Various ground or earth stations are being used in satellite phone communication. These are being used to command and control; in addition to transmission/reception of user signals and also used as Hubs for interconnecting with other communication systems. For example, a satellite phone user wants to make a call to a person who has a mobile phone or wired/landline phone. In this scenario, earth stations play their role and route the communication between these interfacing devices.
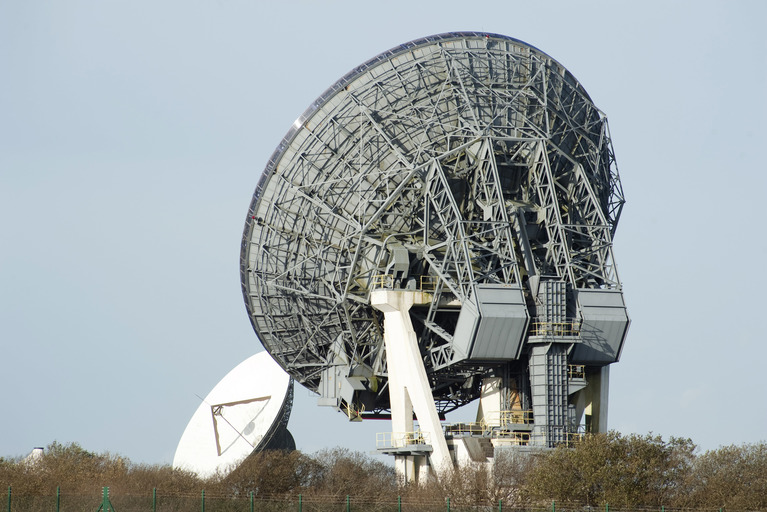

Ground stations for satellite communication
Working of satellite phone:
After discussing these all details we can say that satellite phone is in reality nothing but a radio transceiver. When a user turned on a satellite phone, the signal goes up to any number of satellites in a compatible constellation (GEO or LEO) where it is then registered with the constellation. Those signals are then sent back to ground stations or hubs. The ground stations process and takes care of the switching of the calls rather than the satellite network. These hub stations then direct the call to the Public Switched Telephone Network (PSTN) or a cellular network.
If calling from a wired or mobile phone to a satellite phone, the system works in a reverse manner. Or suppose a user is calling from one satellite phone to another satellite phone. The signal goes up from one satellite phone to the satellite, down to the earth station, back up to a satellite, and then back down to another satellite phone.
Application:
The most common applications of satellite phones are given below:
- Stay connected when there is no other communication medium.
- For remote workers like in hilly areas.
- For disaster response teams.
- For those venturing in the wilderness.
Thanks for reading. See you soon with another exploration!





