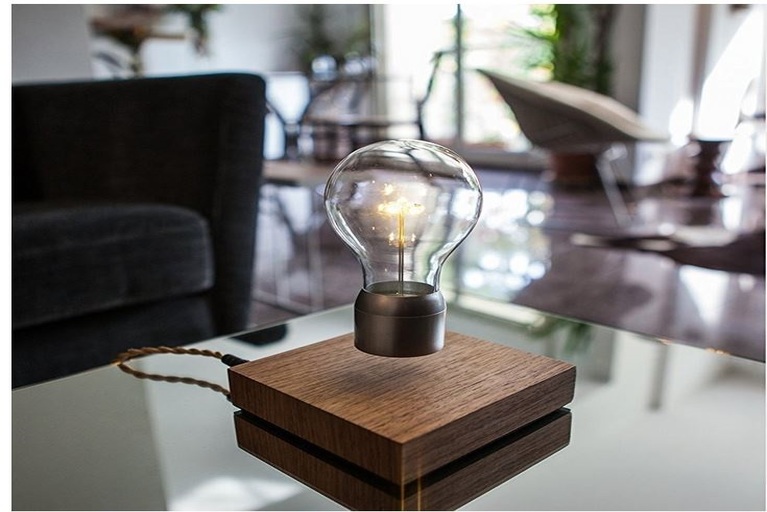
Most of us know about the invention journey of the electric bulb. As we know it has a filament to generate light by using electric current. Generally, common bulbs, CFL or an LED bulb need direct contact with electric conductors to make a glow but what about a bulb those does not need the direct contact with electric current. Sounds cool! Yeah. Today we are going to discuss the same gadget. Now you have a question like what is the name of this object, why we need this kind of thing or what about its life cycle and much more. Don’t worry we are here to clear your doubts. This gadget is known as a magnetic levitating bulb.
What is a Magnetic levitating bulb?
In our school experiments, most of us learn that similar magnetic pole of two different magnets repels each other and opposite attracts. This is the basis of the magnetic levitation system. In the early 20th century a great scientist “Nikola Tesla” invented a tremendous principle. It was known as electromagnetic induction. A Swedish designer Simon Morris combined the magnetic levitation principle with “Nikola Tesla” induction laws and made a model of levitating bulb “FLYTE”.
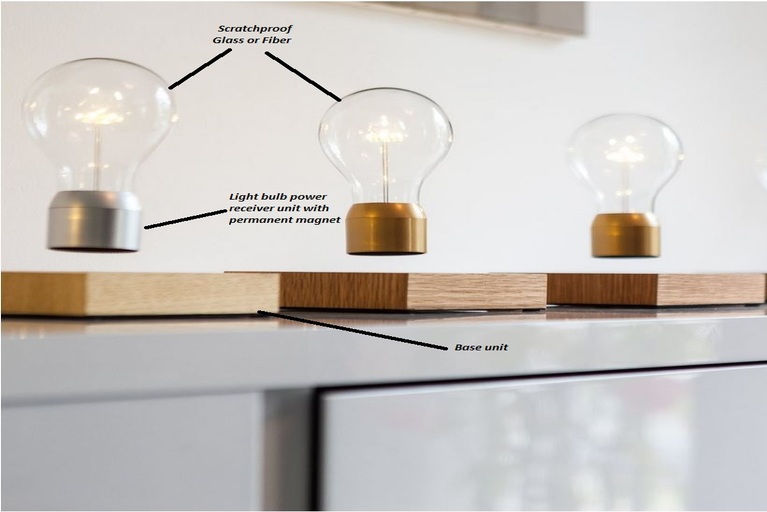
Levitating Bulb
Engineering inside this:
The magnetic levitating bulb or generally known as levitating bulb mainly contains the following parts:
- Base
- Light bulb
Base:
Case of the base is generally made of wood like walnut and oak. The base is having a wireless power transmitter unit that can charge your smartphone also. For this, you just need to put your phone over the base. This unit contains below electronics hardware:
- Electromagnets
- Control board and sensors
- Power adapter
Electromagnets:
To understand the working of this levitating symbol, we need to understand the operation principles of electromagnets. The electromagnet is made of a solenoid tube that has a magnetic core. The core is made of ferromagnetic materials, like iron. Although solenoid can produce magnetic fields even without the magnetic core in this case produced magnetic fields are not strong.
The shape of the magnetic field primarily depends on the shape of the coil which is present over the solenoid tube. In general, several types of electromagnets exist for example, there is a toroidal electromagnet and its magnetic field is different from solenoid magnetic field. The selection of a correct electromagnet is very important. Electromagnet of the base unit needs a high-value current that cannot be provided by using a microcontroller-based control board. To handle the high current a dedicated transistor is being used which is controlled by the control board.
Control board and sensors:
This gadget uses a microcontroller-based control circuit to handle the current of electromagnets and sensors. A specific program has been placed into the microcontroller to trigger the current driver (it is a transistor that provides current to electromagnets of the Base unit) and sensors to detect the motion that turns ON and OFF the power transmission towards the receiver (Light bulb).
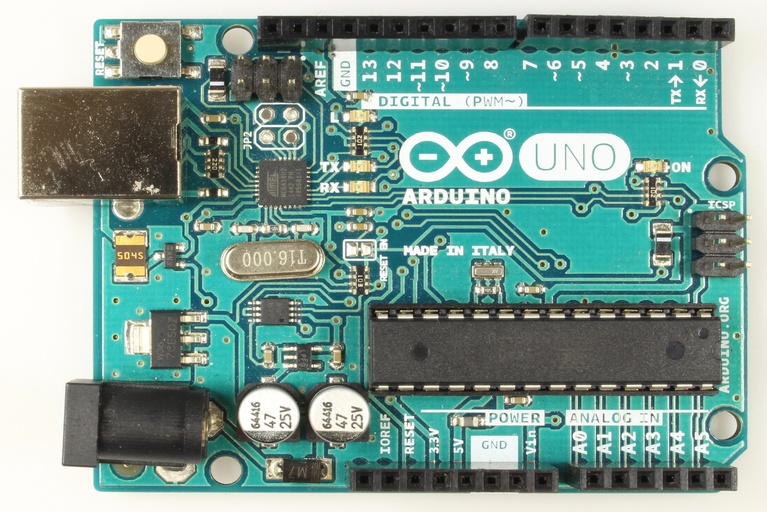
Arduino-UNO as control unit
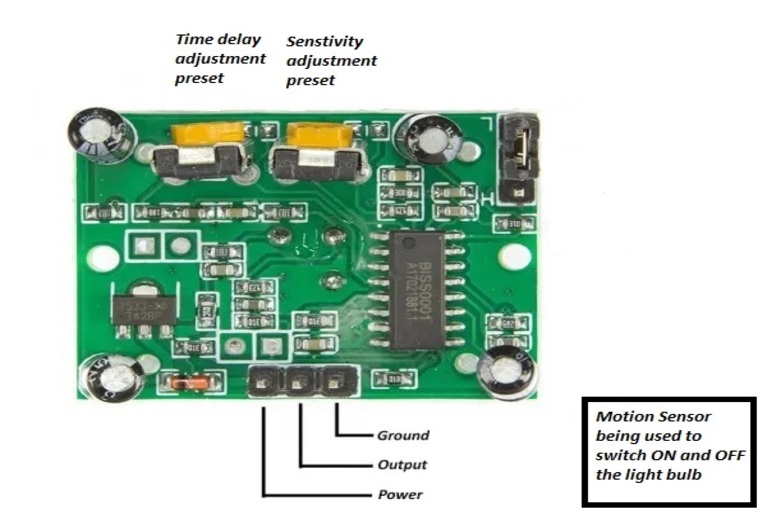
PIR motion sensor use as a switch
Nowadays many control boards are present in the market. But its selection has been mainly depending on the functionalities (like remote controlling, wireless connectivity with smart devices, etc.) of the levitating bulb. For example, Arduino-UNO is a good choice for the control unit.
Power adapter:
The unit provides a power supply to the Base unit. Power adapters are designed to convert the input AC to output DC. It delivers power to the control board, sensors, and current driver. Power adapters are chosen based on their load.
Light bulb:
This bulb contains LEDs to generate light. As we know LEDs are having a long life, good power efficiency, and better durability. The light bulb has a coil to receive power from the Base unit and a permanent magnet to levitate the bulb. It also contains some voltage regulator IC’s to control the input current of LEDs.
Levitating mechanism:
So, as of now, we understand wireless power transmission, reception, and control. Now the secret behind the levitating mechanism of the light bulb is magnets. Both, the Base and Light bulb contains the magnet. The Light bulb contains a permanent magnet whereas the Base contains electromagnets. The electromagnets generate two types of magnetic force. The fringe magnetic force of the electromagnets serves to attract the bulb while the inward magnetic force makes a repelling force. This is what holds the levitating bulb set up and makes it glide approximately 3 to 4 centimetre over the Base unit.
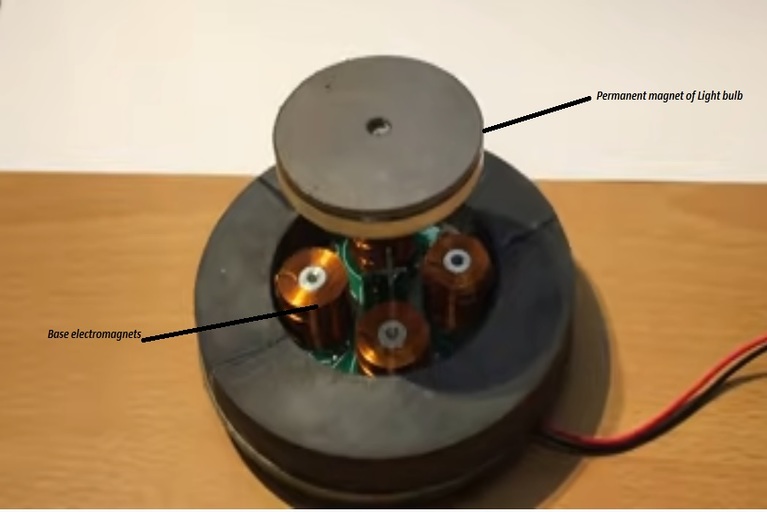
Magnetic levitating mechanism
Working process:
As we have seen magnetic levitating bulb contains two separate parts. The first one is the Base unit that transmits power to the second part, which is a Light bulb. Being installed over the Base, the Light bulb can remain levitating till the power supply is available to the base unit. And also the light bulb can rotate continuously in the air without any friction. To turn it into an ON state you just need to touch the Base unit that activates the motion sensors and vice versa. The bulb light may remain in an ON or OFF state while magnetic levitation remains intact.
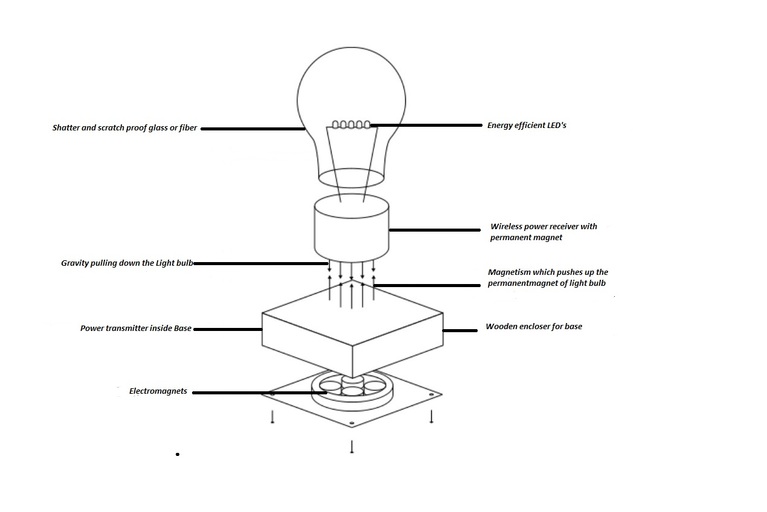
Working diagram of levitating bulb
Limitations:
The main limitation of the magnetic levitating bulb is that only low power transmission is possible in 3 to 4 centimetre distance. Because of this, it can generate a small amount of light which is used only for decoration purposes.
Thanks for reading. See you soon with another exploration!