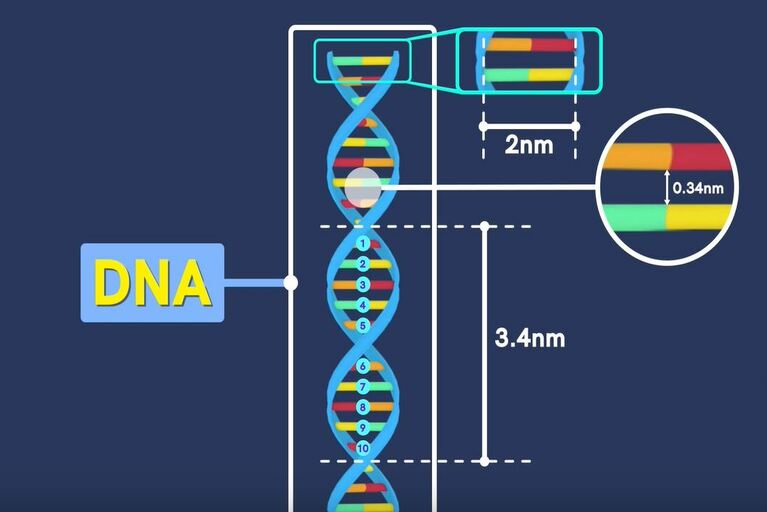
The Discovery of DNA (Deoxyribonucleic acid) changes the world because human beings found a key to knowing their past more accurately. Most of us know that American biologist James Watson and English physicist Francis Crick discovered the DNA but the case is different. DNA was first identified in 1860 by Friedrich Miecher. He was a Swiss chemist. Later on in the chain of discovery other scientists, Phoebus Levene and Erwin Chargaff carried out several experiments to dig this mystery box. At the end of the chain, Watson Crick successfully uncovered DNA and found that DNA is a kind of long molecule that contains each person’s unique genetic code. It holds the instructions for making the proteins essential for the body’s functionality.
DNA Presence and Structure:
DNA is found in almost all living cells whereas its location within a cell varies based on the nucleus. All organisms are composed of cells that either contain nuclei or not. Cells those are containing nuclei are classified as eukaryotic and those are not known as prokaryotic. In eukaryotic cells, DNA is housed within the nucleus but in the case of prokaryotic cells, DNA is located directly within the cellular cytoplasm because the nucleus is absent.
DNA carries information about your physical characteristics as per your ancestors like height, weight, body structure, etc. These physical properties are mainly determined by proteins. And DNA contains the instruction set for making proteins. In DNA, each protein is encoded by gene. Gene is a specific sequence of DNA nucleotides that specify how a single protein is to be made. When nucleotides join together in a series, they form a structure known as a polynucleotide. DNA is often found as stranded polynucleotide either single-stranded or double-stranded.
The main components in DNA are given below:
- A phosphate molecule
- A sugar molecule (Deoxyribose, containing five carbon atoms)
- A nitrogen-containing region
The nitrogen-containing regions known as bases are adenine (A), cytosine (C), guanine (G), and thymine (T). Order these four bases forms the instruction sets for making proteins or genetic codes.
The bases of the two strands of DNA are joined together to create a ladder-like structure. In this ladder, Adenine (A) creates a bond with Thymine (T) and Guanine (G) creates a bond with Cytosine (C). This bond is a hydrogen bond.
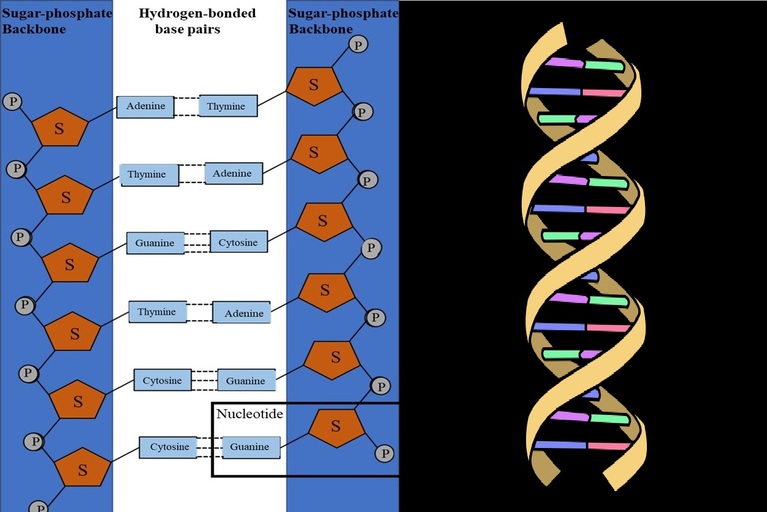
DNA internal structure
How does DNA Function?
Most of the DNA lives in the nuclei of cells whereas some of them exist in mitochondria (the powerhouse of the cell). Strands of DNA loop, coil, and wrapped around proteins, which are known as histones. The Coil state of DNA is known as chromatin. In structured form, this chromatin is called chromosomes. Every chromosome contains one DNA molecule. In human beings, 23 pairs of chromosomes (46 chromosomes) are present whereas in other organisms contain different numbers.
Protein generation in DNA:
The Gene of DNA produces the protein in two ways:
- Transcription: In this procedure, DNA code duplicates into mRNA (messenger RNA). RNA (Ribonucleic acid) is a copy of DNA but it is single-stranded. Also, RNA does not contain base Thymine (T).
- Translation: The mRNA translates into amino acids by tRNA (transfer RNA)
Telomeres:
Telomeres are regions of repeated nucleotides at the end of every chromosome. Its main duty is to protect the end of the chromosome from being damaged by other nearby chromosomes. When a person becomes older, this protective region steadily becomes smaller. Whenever a cell divides and DNA is replicated, the telomere becomes shorter.
Modern Applications of DNA:
DNA is unique to every organism, and therefore it can be used for identification purposes. Human DNA is inherited from their parents: 23 chromosomes from the mother and 23 chromosomes from the father. In the modern world, there are many applications of DNA; some of them are given below:
- Cloning: It is a method used to make an identical copy of an entire multicellular organism. In cloning both original and clone organisms have identical DNA, similar to identical twins.
- In Treatment: At present scientists have developed treatments for genetic diseases and it becomes possible only because of genetic engineering on DNA.
- Genetically modified organisms: A genetically modified organism (GMO) is any organism whose genetic material has been designed using genetic engineering. By using this technique scientists have developed high-yield crops such as wheat, rice, cotton, sunflower, etc.
Thanks for reading. See you soon with another exploration!