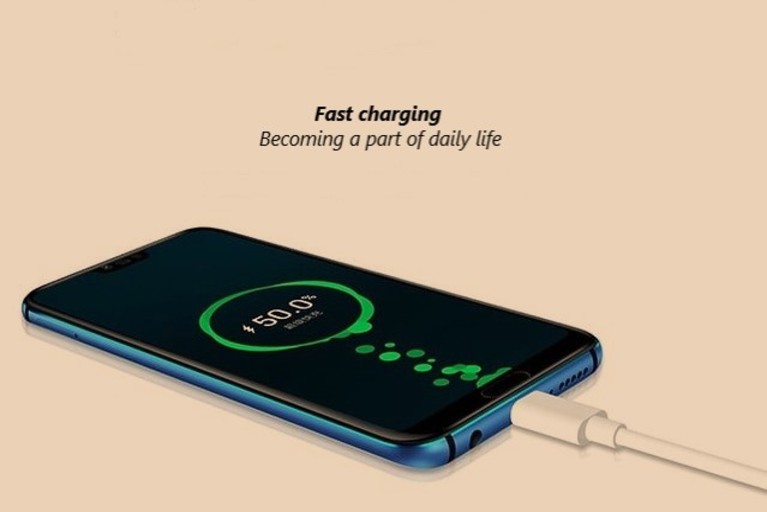

In the present modern technological era, most of the mobile phones are supporting fast charging and that charge the phones within a matter of minutes whereas earlier it used to take hours. The widespread adoption of fast charging in mobile phones increases its use. As mobile phone sizes are getting bigger each year, they need bigger batteries (high mAh) for long time operation. Without fast charging, we would have to wait hours for our phones to top up.
At the most basic level, fast charging is simply increasing the number of watts (W) that are delivered to a mobile battery. A general USB port sends 2.5 W to the connected device, and fast chargers raise this amount.
What is fast charging?

Mobile fast charging
The output of a charger is measured in terms of current and voltage. Multiplying the value of output current and voltage gives you wattage, the measure of total power.
To enable fast charging in mobile chargers most of the manufacturers either boost the output current or vary the voltage to increase the amount of the potential energy or output power. The amount of fast charging standards typically varies the output voltage rather than boost the current.
To enable fast charging in mobile chargers most of the manufacturers either boost the output current or vary the voltage to increase the amount of the potential energy or output power. The amount of fast charging standards typically varies the output voltage rather than boost the current. While using fast charging keep in mind that your device will only take in as much power as its charging circuit is designed for.
Units involved in fast charging of mobile phones:
For proper fast charging of a phone, you need a mobile phone with a charging circuit capable of using one of the fast charging standards, and an adapter and cable enabled for the same standard. We are going to discuss these units one by one.
Charging circuit in phone:
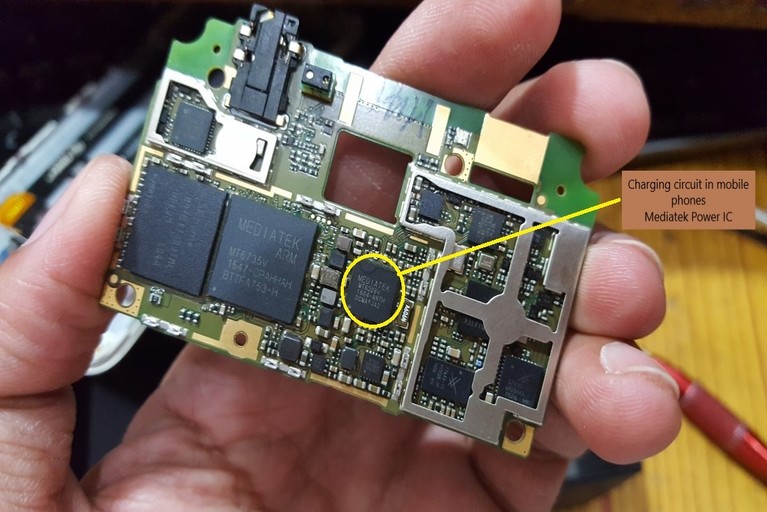
Power IC or Charging circuit on phone
A charging circuit or section in a mobile phone is the section that helps to charge the battery. This circuit is primarily controlled by using the Charging IC or Power IC.
The power IC is an important microchip found in mobile phones. This electronic component is responsible to distribute the required value of current and voltage to all other parts of the mobile phone. The charging section is a part of the power section in a mobile phone PCB.
Mobile phone charger:

Charger and USB for fast charging
This unit plays a main role in fast charging. Most of the mobile manufacturers are providing their own high-power output mobile chargers for smartphones or mobile phones. As we have already discussed the way to make fast charging, either by increasing the output current value or vary the output voltage. We can see it in trending smartphone chargers. Most of the mobile chargers are having high output current (in mA) to enable fast charging. To understand the working of fast chargers, we first need to know how a Li-ion battery of a mobile phone is charged.
Lithium-ion batteries are not charging in a linear manner. When a user connects their mobile phone to the charger the battery charges from 2 volt to a peak voltage of 4.2 volt in two phases.
In the first phase of charging (0% to 50%), the highest peak current and voltage are drawn to the battery and it remains constant throughout this phase. Thus, most of the fast charging technologies are most effective when your battery charge level is less than 50%. After 50%, the output current of the fast charger begins to fall.
The second phase begins when the battery has received most of the charge. The charge controller (power IC) decreases the voltage and current drawn which prevents the phone from overheating and ensuring the smartphone remains safe. Because of this in most smartphones, support fast charging, after 80% charging become slow. For the amount of voltage and current to be passed, the charge controller circuit is used inside the phone. In most smartphones temperature sensors are also present to show the health status of the battery.
The basic USB charger sends 5V and 500mA to 1000mA at the output which is just 2.5 watts to 5 watts. Whereas fast chargers supply more than 10 watts (that is 5 volt and 2 ampere output). Every fast charger uses a common concept and that is supplying more power.
But does more voltage harm your mobile phone battery? For this, fast chargers use a buck converter. It is also known as a switched-mode step-down power supply which lowers the output voltage and increases the output current. More value of the current rapidly fills up your phone battery with charges.
Charging cable:
Can any USB cable support fast charging? The answer is NO. Every USB cable model has its specification like voltage and current handling capacity. Some of the fast chargers support micro-USB cable whereas some of them support Type-C USB cables.
Fast charging standards:
There are two well-known types of fast chargers:
- USB power delivery
- Qualcomm quick charge
USB power delivery:
This standard had published in 2012. USB power delivery implements a data protocol to communicate between a smartphone and a charger. USB Type-C ports can be configured in fast charging modes at 1.5A or 5.0A for more power. USB power delivery offers the following features:
- Increased power levels from existing USB standards
- Power direction is no longer fixed
- Optimize power management across multiple peripherals and interfaces
- Allows low power cases
- Intelligent and flexible system-level management of power
Qualcomm quick charge:
The amount of power to apply the battery is decided by the charge controllers inside the phones. Charge controllers are on-chip in Qualcomm processors, not all Qualcomm processors have charge controllers but smartphones that support fast charging needs to have this charge controller or power IC.
Future of fast charging:
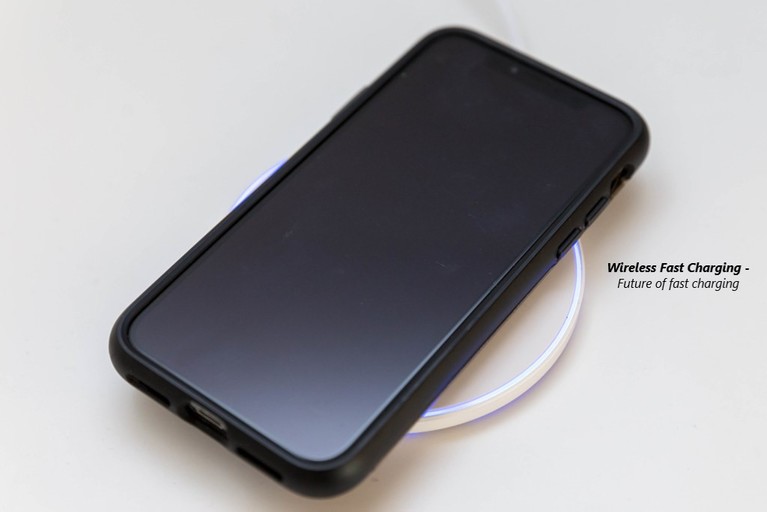

Wireless fast charging
As we know wireless charging is convenient, but it can be slow. Most wireless chargers that lack cooling systems are limited to charging speeds of just 5 volt/1 ampere.
But various manufacturers now offer fast charging pads that come with built-in cooling fans to dissipate heat, allowing you to charge at speeds nearly on par with a cable.
Thanks for reading. See you soon with another exploration!




[…] Wireless charging is slower as compare to direct cable charging, especially in the case of smartphones those are supporting fast charging. […]